How the National Grid works
National Grid power sources
Electricity is generally generated and fed into the National grid in alternating current (AC), typically at 275 or 400 kilovolts (kV), via step-up transformers.
In the UK our electricity comes from a range of sources and the exact mix varies on a daily basis. The main sources are gas fired power stations, wind turbines, nuclear power stations, biomass, coal, solar, imports, hydro and storage. See monthly reports of the UK energy mix.
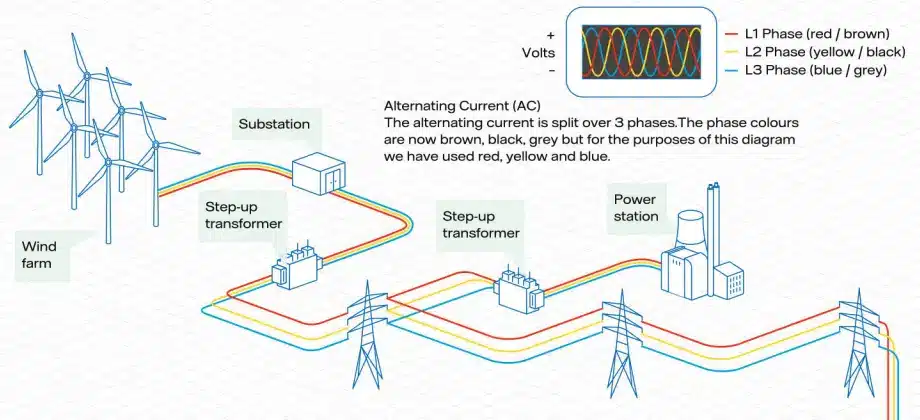
National transmission network
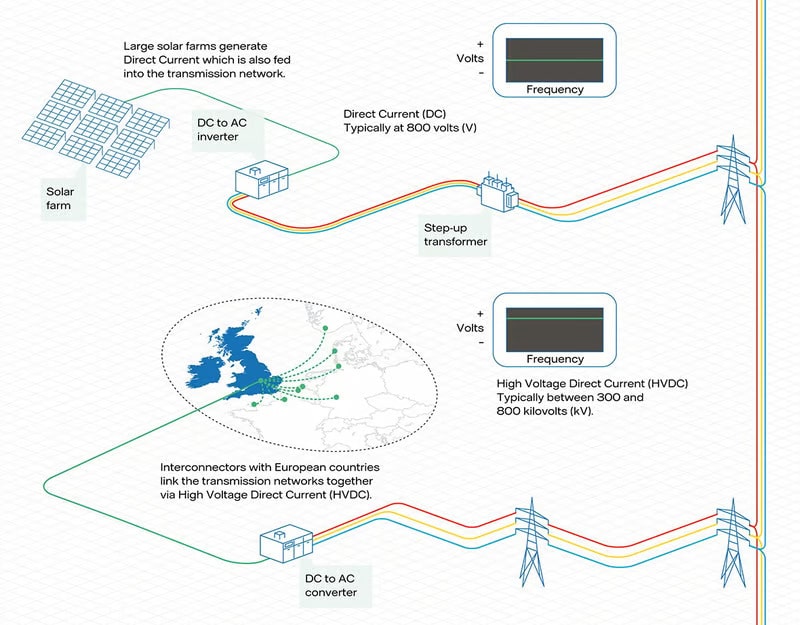
The national transmission network operates at extra high voltages (EHV) of 275 or 400 kilovolts (kV) and is managed by National Grid. Large solar farms generate Direct Current which is also fed into the national transmission network. Interconnectors with European countries link the transmission networks together via High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC).
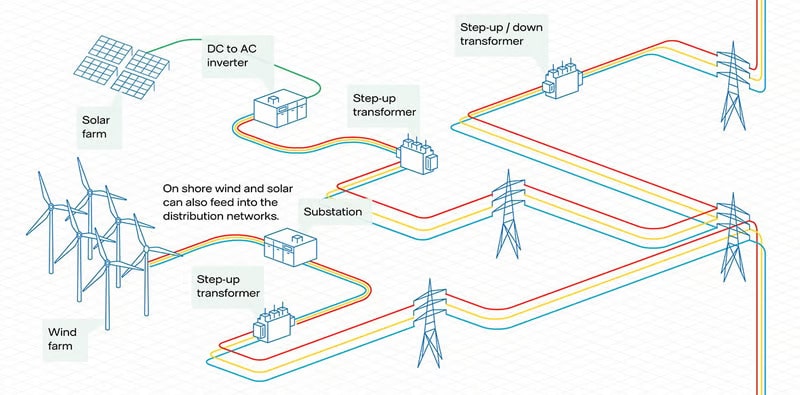
Distribution networks
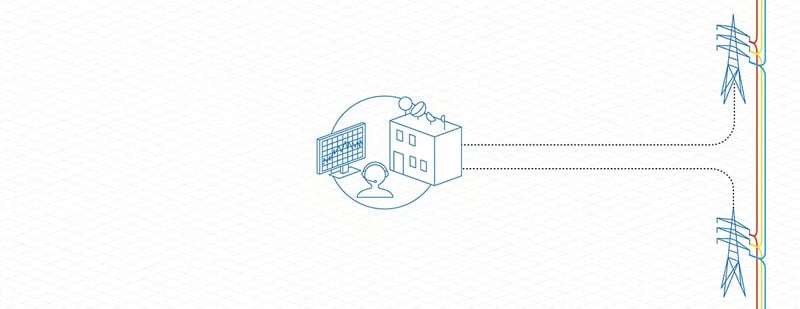
National Energy System Operator
The National Energy System Operator (NESO) balances supply and demand. They operate the system but are not responsible for the infrastructure.
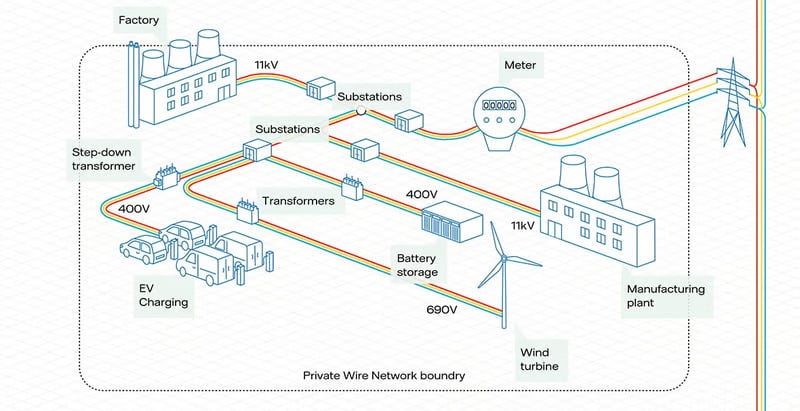
Private wire networks
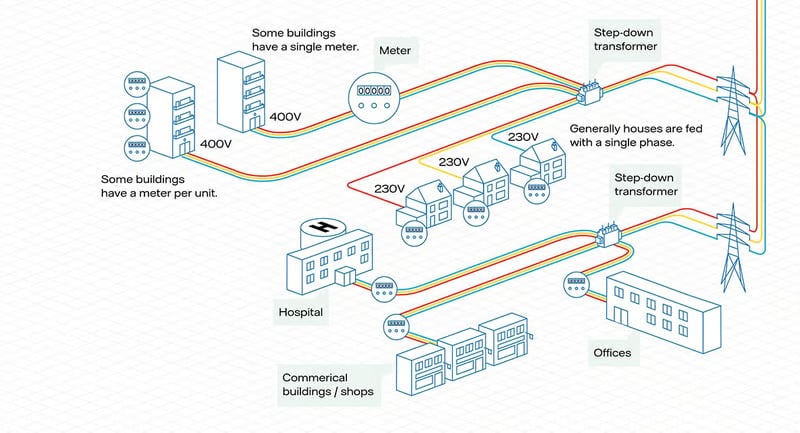
Consumer demand
Download
Download a PDF of the full infographic explaining how the National Grid works.